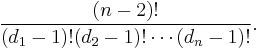Prüfer sequence
In combinatorial mathematics, the Prüfer sequence (also Prüfer code or Prüfer numbers) of a labeled tree is a unique sequence associated with the tree. The sequence for a tree on n vertices has length n − 2, and can be generated by a simple iterative algorithm. Prüfer sequences were first used by Heinz Prüfer to prove Cayley's formula in 1918.[1]
Contents |
Algorithm to convert a tree into a Prüfer sequence
One can generate a labeled tree's Prüfer sequence by iteratively removing vertices from the tree until only two vertices remain. Specifically, consider a labeled tree T with vertices {1, 2, ..., n}. At step i, remove the leaf with the smallest label and set the ith element of the Prüfer sequence to be the label of this leaf's neighbour.
The Prüfer sequence of a labeled tree is unique up to isomorphism and has length n − 2.
Example
Consider the above algorithm run on the tree shown to the right. Initially, vertex 1 is the leaf with the smallest label, so it is removed first and 4 is put in the Prüfer sequence. Vertices 2 and 3 are removed next, so 4 is added twice more. Vertex 4 is now a leaf and has the smallest label, so it is removed and we append 5 to the sequence. We are left with only two vertices, so we stop. The tree's sequence is {4,4,4,5}.
Algorithm to convert a Prüfer sequence into a tree
Let {a[1], a[2], ..., a[n]} be a Prüfer sequence:
The tree will have n+2 nodes, numbered from 1 to n+2. For each node set its degree to the number of times it appears in the sequence plus 1. For instance, in pseudo-code:
Convert-Prüfer-to-Tree(a) 1 n ← length[a] 2 T ← a graph with n + 2 isolated nodes, numbered 1 to n + 2 3 degree ← an array of integers 4 for each node i in T 5 do degree[i] ← 1 6 for each value i in a 7 do degree[i] ← degree[i] + 1
Next, for each number in the sequence a[i], find the first (lowest-numbered) node, j, with degree equal to 1, add the edge (j, a[i]) to the tree, and decrement the degrees of j and a[i]. In pseudo-code:
7 for each value i in a 8 for each node j in T 9 if degree[j] = 1 10 then Insert edge[i, j] into T 11 degree[i] ← degree[i] - 1 12 degree[j] ← degree[j] - 1 13 break
At the end of this loop two nodes with degree 1 will remain (call them u, v). Lastly, add the edge (u,v) to the tree.[2]
14 u ← v ← 0 15 for each node i in T 16 if degree[i] = 1 17 then if u = 0 18 then u ← i 19 else v ← i 20 break 21 Insert edge[u, v] into T 22 degree[u] ← degree[u] - 1 23 degree[v] ← degree[v] - 1 24 return T
Cayley's formula
The Prüfer sequence of a labeled tree on n vertices is a unique sequence of length n − 2 on the labels 1 to n — this much is clear. Somewhat less obvious is the fact that for a given sequence S of length n–2 on the labels 1 to n, there is a unique labeled tree whose Prüfer sequence is S.
The immediate consequence is that Prüfer sequences provide a bijection between the set of labeled trees on n vertices and the set of sequences of length n–2 on the labels 1 to n. The latter set has size nn−2, so the existence of this bijection proves Cayley's formula, i.e. that there are nn−2 labeled trees on n vertices.
Other applications
- Cayley's formula can be strengthened to prove the following claim:
- The number of spanning trees in a complete graph
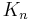 with degrees
with degrees 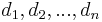 is equal to
is equal to
- The proof follows by observing that in the Prüfer sequence number
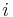 appears exactly
appears exactly 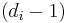 times.
times.
- Cayley's formula can be generalized: a labeled tree is in fact a spanning tree of the labeled complete graph. By placing restrictions on the enumerated Prüfer sequences, similar methods can give the number of spanning trees of a complete bipartite graph. If G is the complete bipartite graph with vertices 1 to n1 in one partition and vertices n1 + 1 to n in the other partition, the number of labeled spanning trees of G is
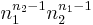 , where n2 = n − n1.
, where n2 = n − n1.
References
- ^ Prüfer, H. (1918). "Neuer Beweis eines Satzes über Permutationen". Arch. Math. Phys. 27: 742–744.
- ^ Jens Gottlieb, Bryant A. Julstrom, Günther R. Raidl, and Franz Rothlauf. (2001). "Prüfer numbers: A poor representation of spanning trees for evolutionary search". Proceedings of the Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference (GECCO-2001): 343–350. http://www.ads.tuwien.ac.at/publications/bib/pdf/gottlieb-01.pdf.
External links
- Prüfer code – from MathWorld